How does EDTA Chelation therapy work? (Part one)
Comments Off on How does EDTA Chelation therapy work? (Part one)
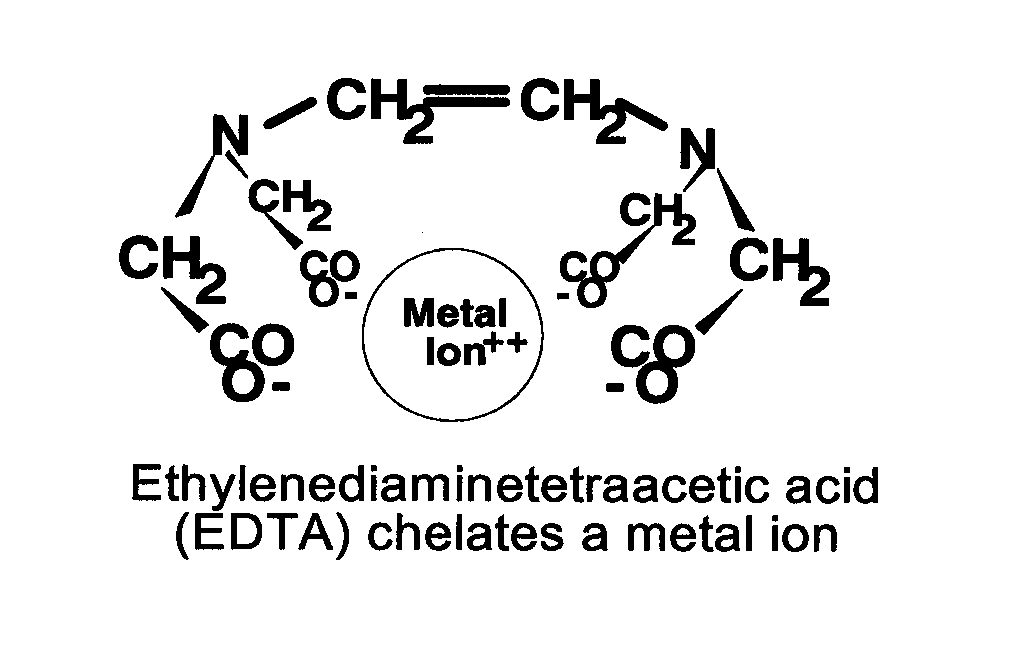
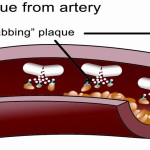
Many theories have been put forward for consideration [to explain how EDTA Chelation works.] One of the more common explanations is that EDTA binds to the calcium in arterial plaques and removes it, thus breaking up the plaque.
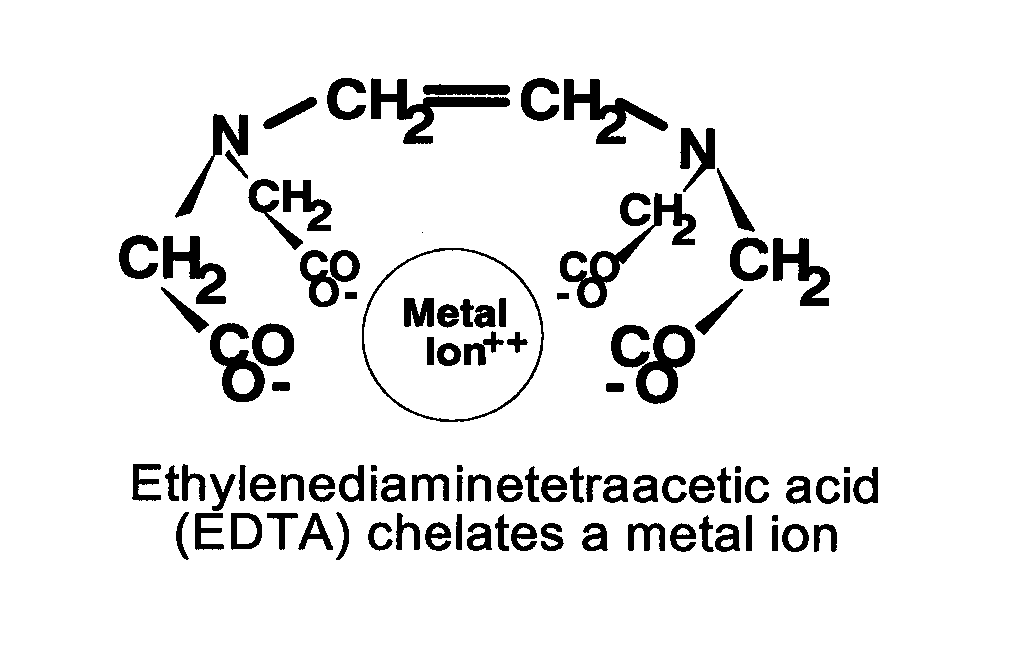 Some people express concern over the binding of calcium, thinking that this process must also strip away calcium from the bones and teeth. Proponents of the theory explain that the calcium is only removed from inappropriate locations such as the arteries. Garry Gordon, M.D., D.O., adds that the binding of calcium is actually good for the bones. Reduced serum calcium levels stimulate the parathyroid gland to secrete parathormone, which not only causes the restoration of appropriate calcium levels but also activates bone-strengthening osteoblasts, effectively reversing the course of osteoporosis.
Some people express concern over the binding of calcium, thinking that this process must also strip away calcium from the bones and teeth. Proponents of the theory explain that the calcium is only removed from inappropriate locations such as the arteries. Garry Gordon, M.D., D.O., adds that the binding of calcium is actually good for the bones. Reduced serum calcium levels stimulate the parathyroid gland to secrete parathormone, which not only causes the restoration of appropriate calcium levels but also activates bone-strengthening osteoblasts, effectively reversing the course of osteoporosis.
Cranton, however, rejects the whole theory of removing calcium from plaques as outdated. He favors explanations involving more recent research into the area of free radical pathology. Cranton explains that free radicals can disrupt many other important molecules around them and have been implicated in the promotion of atherosclerosis, cancer, and the basic decline in human health with age. He says that EDTA binds to and removes a particular form of iron that can catalyze the formation of free radicals.